Whether it’s plastic containers, clothes, home appliances, the detergents and medicines we use, the transport we choose or the heating in our homes, countless everyday objects and business processes require petroleum-derived substances for their operation or manufacture.
As a result, oil refineries are essential for producing the raw materials we need to make both our home and work lives easier in any social or economic sphere.
Refineries are industrial plants that employ a range of chemical processes to transform crude oil into useful products. Once refined, these products then become highly valuable because of their wide range of potential uses in other industrial processes.
At the same time, these refining processes are one of the most significant contributors to air pollution (Galvan, L.E., 2007), both near the facility and further afield, and can dramatically worsen the air that we all breathe.
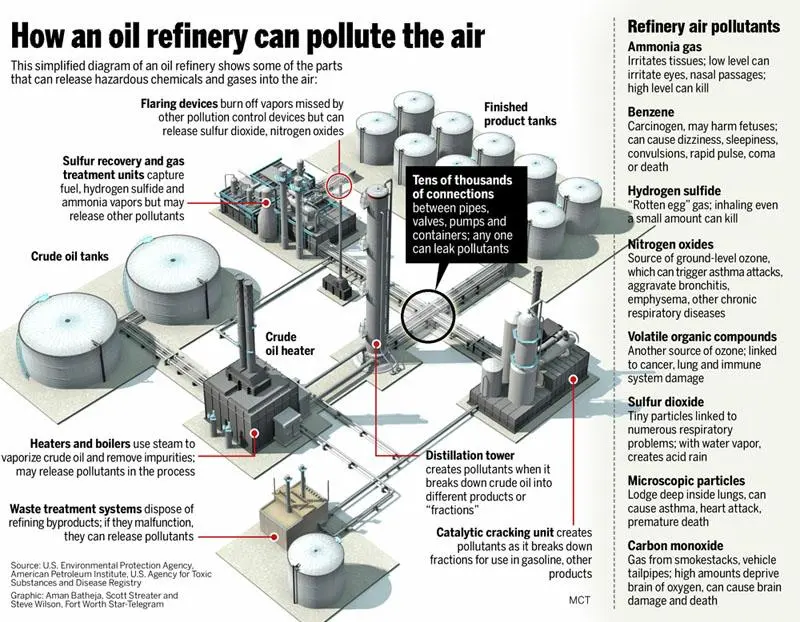
These various oil refining processes are the oil industry’s principal source of air emissions. They release gases such as carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds into the air, as well as emitting high concentrations of a harmful combination of small chemicals in both a solid and liquid state, known as suspended particles or particulate matter.
In 2022, the world’s oil refinery capacity almost reached 102 million barrels per day. Overall, global refinery capacity has nearly doubled in the past fifty years, experiencing the largest growth during the 1970s.
What are oil refinery emissions?
The oil industry is one of the most regulated sectors worldwide, and its atmospheric emissionsAtmospheric emissions are pollutants emitted into the air, mainly as a result of human activities such as industry, transport by combustion vehicles and en...
Read more are strictly controlled by the environmental laws of many countries. However, despite existing legislation, it is essential for refineries to implement innovative processes to minimise the environmental impact of producing refined petroleum products. This is because refineries can generate a wide range of toxic chemicals, many of which are harmful to human health and the environment.
Air Quality Innovation in Just 1 Click
Stay informed about the air you breathe!
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest updates on environmental monitoring technology, air quality studies, and more.
The emissions from oil refineries mainly originate from crude oil refining processes, including distillation, hydrotreating, and reforming. These activities release volatile compounds, such as hydrocarbons, greenhouse gasesWhile the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere has been steadily and rapidly increasing in recent decades, in May 2025, CO2 surpassed 43...
Read more (CO2, CH4), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and sulphur dioxide (SO2), among other hazardous pollutants. Furthermore, some of these substances may be invisible to the naked eye, making their monitoring even more critical.
Air qualityAir quality refers to the state of the air we breathe and its composition in terms of pollutants present in the atmosphere. It is considered good when poll...
Read more monitoring in oil facilities using advanced sensors is essential to control emissions from various refining processes. By using real-time monitoring technology, it is possible to obtain reliable and accurate readings, helping to anticipate whether pollutant emissions could exceed established limits and reach the open air. This information is crucial to prevent pollutants from entering the atmosphere, which could have devastating consequences for both the environment and public health.
“The petroleum industry represents one of the chief latent threats for the environment and influences ecosystems and subsequently all living organisms, including human beings.” (Monteiro A. et al., 2017).
The analysis of these measurements, along with their proper management, can prevent harmful impacts on the health of workers in the petrochemical industry and help improve air quality in surrounding areas. Emissions from the petrochemical industry, in fact, can travel hundreds of kilometres from their point of origin, affecting distant communities.
Controlling emissions is not only crucial for public health, but also to protect surrounding natural resources such as water, soil, and local flora and fauna, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Oil and gas extraction processes
Petroleum is a mixture of organic liquids and gases (mainly hydrocarbons) found inside the earth’s crust. The main constituent gas of petroleum is natural gas, which is mostly composed of methane (CH4)Methane, known chemically as CH₄, is a gas that is harmful to the atmosphere and to living beings because it has a high heat-trapping capacity. For this ...
Read more, whereas the main liquid component is crude oil.
The bitumen state of crude oil is the result of millions of years of anaerobic or oxygen-free microbial decomposition of large amounts of dead organisms, built up underground and subjected to high pressure.
The oil industry is the largest industrial sector in the world, refining crude oil and processing natural gas to produce countless useful substances, such as petrol or asphalt, and many others that are used as raw materials in other industrial processes.
During the refining process, which is highly energy-intensive, crude oil is separated into heavy products like tar, less heavy products like diesel and kerosene, and lighter products (which are the most valuable), such as petrol.
Refining techniques require petroleum to be separated into its different components. Then, these components undergo various conversion processes to give each derivative homogeneous characteristics.
While the very first refineries used physical separation processes before moving on to dry and atmospheric fractional distillation techniques, today’s oil industry employs a range of methods based on the use of heat, catalysation, pressure and chemicals. This way, it can comply with current regulations as it transforms oil into the world’s most in-demand petrochemical products.
Environmental impact of oil refineries
Oil refineries are industrial facilities that have a significant environmental impact due to the emission of atmospheric pollutants, the production of toxic waste, and the intensive consumption of water and energy. These complexes release harmful gases that affect air quality, leading to the degradation of ecosystems and climate changes. Additionally, soil and nearby water sources contamination due to spills and industrial discharges is another looming risk, threatening biodiversity and human health. Therefore, controlling industrial emissions is key to minimising these negative effects.
Air pollution from refineries: types of polluting gases
Oil extraction is a complex process that involves several operations based on advanced technologies. This process generates greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). Refineries are the third-largest global emitter of GHGs. The oil industry’s primary environmental harm lies in gaseous emissions (Damian, C., 2013), as it is responsible for 6% of global industrial net emissions.
The air pollution caused by oil refineries is one of the biggest environmental challenges associated with this industry. During the refining processes, polluting gases are released that can severely affect nearby communities and more distant ecosystems, as winds disperse these substances over long distances.
Emissions in a refinery are produced during the cracking of crude oil in different units. Altogether, during refining, there are numerous sources that significantly contribute to air quality deterioration through the emission of:
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)
These are over a hundred substances produced, among other causes, by the combustion of oil, coal, and gasoline. They typically combine with each other and adhere to dust particles. Additionally, they can react with sunlight and other substances suspended in the air. Prolonged and high exposure to PAHs causes skin and eye problems, has a high carcinogenic potential, and weakens the immune system’s ability to fight infections.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2)Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is a colourless gas with a pungent odour that causes an irritating sensation similar to shortness of breath. Its origin is anthropoge...
Read more
Although the sulphur produced as a waste in refineries can be processed in desulphurisation and sulphur recovery plants by 98%, when it is burned, it is emitted into the atmosphere as sulphur dioxide. It is a colourless gas with an unpleasant smell and an irritating capacity, which is also highly toxic and can cause strokes and lung cancer.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
These are yellowish gases with a strong odour derived from the burning of hydrocarbons. Being water-soluble, they form nitric acid (NO2). It is a harmful gas that causes headaches, dizziness, vomiting, and weakness, while also irritating the eyes and respiratory pathways. It can also cause bronchitis and pulmonary oedema and can be a cause of death from prolonged exposure.
Carbon monoxide (CO)The carbon monoxide (CO) is an invisible gas (colorless and odorless) that, at the same time, is a silent killer because in just a few minutes it exhibits ...
Read more
Odourless and flammable, it is a gas that does not cause immediate irritation, so its presence often goes unnoticed. Inhalation leads to mental confusion and dizziness, headaches, and even fainting. Prolonged exposure results in neurological and cardiovascular disturbances.
Hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
With a characteristic rotten egg smell, it is considered, along with CO2, as an acidic gas. It is highly toxic and flammable, and exposure to high levels of H2S leads to death in a short time. When found in lower concentrations in the air, it causes headaches, fatigue, vomiting, breathing difficulties, and irritation of the eyes.
Particulate matter (PM)Atmospheric particulate matter are microscopic elements suspended in the air, consisting of solid and liquid substances. They have a wide range of sizes an...
Read more
Sulphur in the atmosphere, when combined with existing moisture, eventually turns into sulphur trioxide and then forms sulphides and sulphuric acid. These substances, in aerosol form, contribute to an increase in the proportion of toxic particulate matter in the atmosphere, especially those of smaller or fine (PM2.5) and ultrafine (PM1) size. They are the cause of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and also increase the incidence of cancer.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
These are hydrocarbons that remain gaseous at room temperature. They are highly volatile and abundant in the air. The refinery as a whole is the largest emitter of VOCs, and their management must include detection and leak control, as well as good conservation and cleaning practices to prevent them from reaching the atmosphere. They cause smogSmog, beyond that dense fog
Smog is a mixture of air pollutantsAir pollution caused by atmospheric contaminants is one of the most critical and complex environmental problems we face today, both because of its global r...
Read more that accumulate in the atmosphere, especially in urban areas. This phenomenon is character...
Read more or reddish fog that makes the environment unbreathable and contributes to respiratory conditions and cardiovascular accidents. Some VOCs are extremely dangerous to health, affecting the liver, central nervous system, or causing kidney damage and cancer.

Want to control the impact of your processes on air quality?
Download the technical report [PDF] on the air quality control network deployed at the Cemex plant.
Find out how Cemex has managed to control emissions and get the environmental impact of cement production under control.
The amount of emissions produced depends on various factors, including the efficiency of the refinery and the type of oil being refined at its facilities. In general, more modern and efficient refineries tend to produce fewer emissions than older refineries, as they have less optimised and cleaner systems.
Additionally, refineries generate emissions during the process of burning gas used to eliminate residual gases that cannot be recovered or recycled. This activity, in turn, produces emissions, although the amount varies depending on the efficiency of the refinery and the type of gas being burned. (Sojinu, S. O., & Ejeromedoghene, O., 2019).
Main problems caused by air pollution from refineries
Despite their importance in the global economy and the strategic resources they produce for countless sectors, oil refineries have a significant impact on the environment.
As well as requiring vast amounts of energy and natural resources, such as water, they also generate high levels of waste, some of which is toxic. Air emissions are some of the most harmful by-products of the refining process, contaminating not just the air but also soil and water.
Increased amounts of nitrous oxide (N2O) in the air combine with atmospheric moisture to produce acid rain. This, in turn, can cause extraordinary damage to ecosystems, destroying forests and acidifying both inland bodies of water and the ocean. The reduction of the pH of the water, thereby making it more acidic, alters the biodiversity that depends on marine and freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, aquatic organisms are severely affected when polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are deposited in water.
The nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds emitted by refineries react with oxygen in the air, thereby changing levels of atmospheric ozone at ground level. Due to photochemical reactions triggered by strong solar radiation, these nitrogen oxides can lead to high concentrations of tropospheric ozone. Ground-level ozone is considered a very harmful secondary pollutant as it can affect crops, forests, plant development and associated fauna.
Similarly, greenhouse gas emissions from refineries are a significant contributor to climate change. The burning of fossil fuels in these refineries produces large amounts of carbon dioxide, one of the main greenhouse gases. In addition to CO2 emissions, refineries also emit large amounts of methane, a more potent greenhouse gas than CO2 as discussed in our article Methane Pollution: Impact on the Environment, Health, and Solutions.
Net greenhouse gas emissions from refineries are a major environmental concern as they contribute to global warming and severe climate changes, in turn producing phenomena such as violent storms and hurricanes.

Aerial view of oil refineries along the Athabasca River in Canada
Emissions monitoring in refineries: necessity and benefits
Emissions monitoring in oil refineries is crucial to comply with environmental regulations and protect both the environment and public health. This measurement allows for identifying pollutants, such as sulphur oxides (SO₂) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), released during the refining process. Additionally, continuous monitoring facilitates early leak detection, optimises processes, and prevents penalties for non-compliance with environmental legislation, benefiting both companies and surrounding communities.
Industrial air quality monitoringControlling air quality is an essential task in order to enjoy optimal environmental conditions for healthy human development and to keep the environment i...
Read more
Air quality monitoring in refineries is essential to real-time assess the concentration of emitted pollutants. This continuous monitoring allows environmental managers to adjust production processes and reduce the emission of gases such as NOx, SO₂, and VOCs. The adoption of advanced measurement technologies, like those offered by Kunak, ensures compliance with regulations, protects worker health, and minimises environmental impact in areas surrounding the oil facilities.
Pollutant monitoring technology in refineries
Monitoring technology has advanced significantly, offering more precise and easy-to-integrate systems. The Kunak AIR Pro and Kunak AIR Lite stations provide real-time measurements, enabling leak detection and optimising environmental management. With their modular design and interchangeable cartridges for measuring gases such as SO₂, NOx, and VOCs, this technology is vital for air quality control in refineries and for complying with the strictest regulations.
Industrial emissions control in refineries: innovative solutions
Industrial emissions control in refineries requires advanced solutions that include real-time monitoring and advanced analytics. Air quality stationsAir quality stations are systems dedicated to monitoring atmospheric pollution, essential for measuring the concentration of pollutants in a specific area....
Read more capable of measuring pollutants like SO₂, NOx, and particulate matter enable quick detection of emission deviations. Additionally, data management systems facilitate a swift response to unexpected increases, optimising refining processes and ensuring environmental compliance.
Industrial emissions control: challenges and strategies
Industrial emissions control in refineries faces challenges such as variability in production processes and weather conditions that disperse pollutants. To overcome these obstacles, it is necessary to implement comprehensive strategies that include continuous monitoring systems, the adoption of clean technologies, and the optimisation of combustion processes. Additionally, it is crucial to train technical staff in environmental management and data analysis, enabling them to detect critical points and reduce pollutant emissions in oil facilities.
Solutions for industrial emissions monitoring
Solutions for industrial emissions monitoring in refineries have evolved towards intelligent systems capable of real-time measurement of key atmospheric pollutants. Among these, the Kunak AIR Pro and Kunak AIR Lite stations stand out for their precision, reliability, and ease of installation. These stations use a patented system of interchangeable cartridges, with sensors specific to gases such as sulphur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM), among others. This flexibility allows monitoring to be adapted to the needs of each refinery, ensuring accurate data and improving environmental control. Furthermore, their remote management capability facilitates constant supervision and reduces operational costs, positioning Kunak as a leader in industrial air quality control technology.
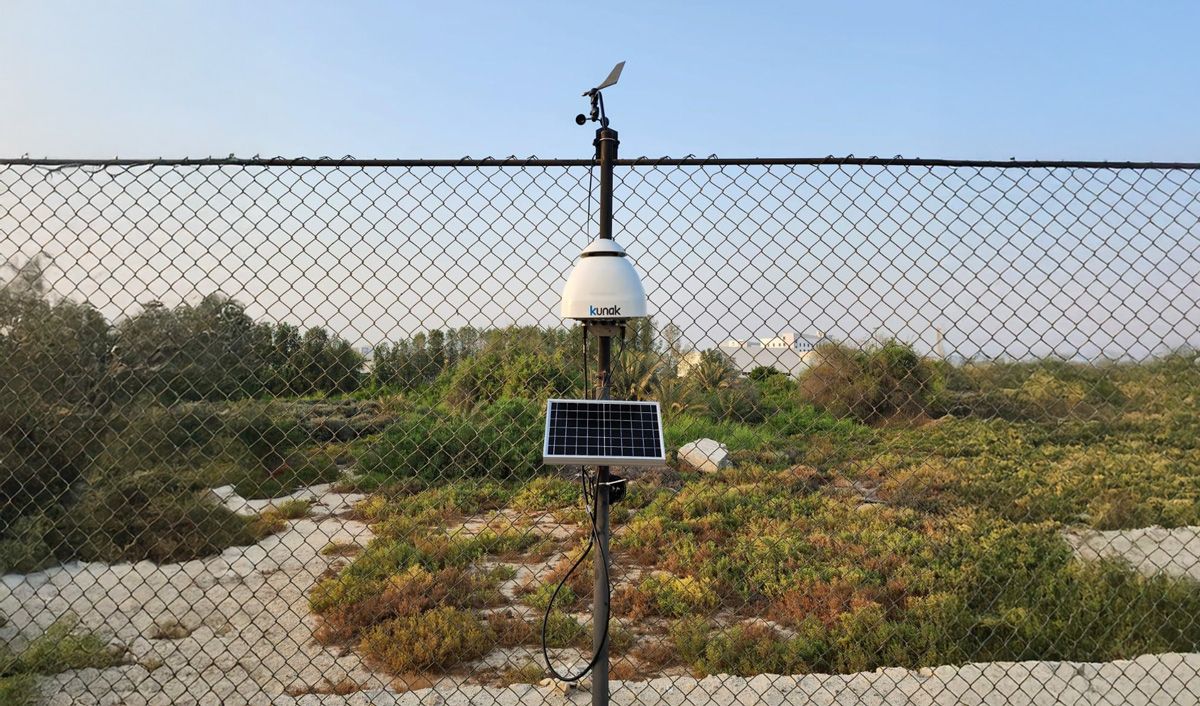

Fenceline outdoor air quality monitoring with Kunak AIR Pro station in Abu Dhabi
Measuring emissions from refineries: tools and advanced techniques
Emissions measurement is essential to ensure sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations. Given the complexity of refining processes, having advanced tools to accurately monitor pollutants is crucial. Current technologies, such as air quality sensorMeasuring air quality is essential for improving human and environmental health. Changes in the natural composition of the air we breathe are common in ind...
Read mores and remote monitoring systems, provide real-time data to assess key pollutants.
Understanding industrial emissions in detail not only reduces environmental impact but also improves the operational efficiency of refineries.
Emissions measurement: importance in regulatory compliance
Complying with environmental regulations is a challenge for refineries, as regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. Measuring emissions in real time allows companies to ensure they do not exceed legal limits, detect deviations, and avoid penalties. Implementing continuous monitoring technologies ensures efficient environmental management, protecting both worker health and air quality in surrounding communities.
Benefits of accurate emissions measurement
Accurate emissions measurement in refineries brings key benefits for companies and the environment. It facilitates compliance with regulations, avoiding penalties and reducing legal risks. It also helps detect leaks and optimise industrial processes, cutting costs. Furthermore, it improves protection of worker health and communities, minimises environmental impact, and enhances corporate reputation.
Reducing emissions in the refining sector
Of all the activities involved in the oil industry (extraction, storage, transport and refining), refineries face the greatest challenge in terms of their net emissions. They contribute towards a reduction in air quality and have a significant impact on the environment, which, in turn, affects their ability to comply with environmental regulations designed to tackle climate change.
While crude oil refining techniques are improving all the time, the growing global demand for a wide variety of petroleum products means that compliance with environmental legislation remains a constant challenge for refineries. Legislation regulates petrochemical operations and also places stipulations on the quality of petroleum-derived products in order for them to be accepted on commercial markets.
This means that it is not just equipment and processes that need to be improved but also the way that facilities are run, including their operation, maintenance and downtime.
Therefore, it is essential to use scientific and technical processes to achieve the following:
- Optimise the use of raw materials. By improving oil refining processes, high-value products, such as petrol or diesel, can give better performance, thereby making them more efficient and cleaner to use.
- Promote energy efficiency. By capturing and using the waste heat produced, making greater use of renewable energies and incorporating innovative refining processes, the amount of energy consumed by refineries can be reduced.
- Reduce atmospheric emissions. The most modern refineries incorporate industrial practices and technologies that minimise the emissions produced. Such emissions are directly linked to the alteration of ecosystems and the acceleration of climate change, as well as having a chronic impact on human health.
- Reduce the amount of waste generated. Waste and by-products from oil refineries are a dangerous source of pollution. As well as affecting air quality, they can also contaminate soil and water, thereby damaging ecosystems and causing serious environmental problems.
- Monitor and control emissions. Regular, real-time monitoring of emissions produced at each stage during the refining process, using devices such as Kunak sensors, allows the early detection of suspended gases and particulates that can affect air quality. This is the most effective way to optimise refining operations, identify issues quickly, such as possible gaseous leaks or process anomalies, and reduce the impact of refineries on air quality.
- Promote the use of new technologies. The oil refining sector is implementing innovative measures to promote sustainability, such as the use of technologies to safely capture and store tonnes of carbon for future use and the promotion of global decarbonisation. The oil industry is also incentivising the transition towards cleaner sources of energy, such as biofuels and green hydrogen.
The modern oil industry will face a major challenge in the coming decades to balance the economic benefits of oil with the resulting environmental damage. (Al-Rubaye, A.H., et al. 2023).
To successfully transition to a global low-emission economy and help curb climate change, it is important to have cleaner, more efficient oil refineries. (Granda, M.L., 2023) that continuously adhere to good management and business practices, are committed to sustainable development and comply with the environmental measures in force.
Success stories: implementation of Kunak sensors in refineries
In 2023, Kunak carried out a key project deploying a continuous environmental monitoring network at an oil facility in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. A leading company in the oil & gas sector trusted Kunak AIR Pro stations to ensure regulatory compliance and protect air quality in nearby communities.
A network of four solar-powered stations was deployed, capable of measuring in real-time pollutants such as sulphur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NO₂), ozone (O₃), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM). The devices, equipped with sonic anemometers, help to identify emission sources and respond quickly to potential exceedances.
Thanks to Kunak’s technology, the client ensures that their operations meet environmental standards, consolidating their commitment to the health of workers and the wellbeing of the local population.
FAQs about oil refinery emissions
Why is it important to monitor emissions from oil refineries?
Monitoring emissions from refineries is crucial to minimise environmental impact and protect public health. These facilities emit pollutants such as sulphur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM), which can severely affect air quality. Continuous measurement allows for detecting leaks, preventing legal limit exceedances, and optimising industrial processes. Additionally, it facilitates compliance with environmental regulations and reduces the risk of penalties. Without proper monitoring, uncontrolled emissions could cause irreversible damage to nearby ecosystems and increase the risk of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in surrounding communities.
What technologies are used to control industrial emissions?
Industrial emissions control is based on the combination of capture, treatment, and monitoring technologies. Among the most commonly used are gas purification systems, such as wet scrubbers and baghouse filters, which reduce particulate matter and pollutants. Simultaneously, air quality monitoring relies on gas sensors and continuous emission measurement systems (CEMS), which provide real-time data on emissions of SO₂, NOx, CO, VOCs, and PM. These technologies not only ensure regulatory compliance but also optimise refinery operational efficiency by detecting leaks and enabling quick decision-making to reduce environmental impact.
How do refinery emissions affect the environment and human health?
Refinery emissions release pollutants such as sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds, which negatively impact both the environment and human health. These gases contribute to acid rain, smog, and global warming, as well as affecting biodiversity. For humans, prolonged exposure to these pollutants can cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases and increase cancer risks. Communities near refineries are the most vulnerable, experiencing higher rates of asthma and other lung conditions. Therefore, rigorous emissions control is essential to protect the environment and ensure quality of life.
What regulations must refineries comply with regarding emissions?
Refineries must comply with strict environmental regulations at international, national, and regional levels. In the United States, key regulations include those from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), such as the Clean Air Act, which sets limits on pollutants like SO₂, NOx, and VOCs. In the European Union, the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) requires the implementation of the best available techniques (BAT) to reduce emissions. Specific limits are also imposed on particulates, toxic gases, and carcinogenic compounds. Compliance with these regulations mandates refineries to implement advanced measurement and control technologies, ensuring sustainable and safe operations.
How do Kunak sensors contribute to emissions control in refineries?
Kunak sensors are key tools for emissions control and monitoring in refineries, thanks to their precision and real-time measurement capability. The Kunak AIR Pro and Kunak AIR Lite stations can detect gases such as SO₂, NOx, CO, VOCs, and particulate matter, providing reliable data that helps refineries comply with environmental regulations. Their interchangeable cartridge system allows adaptation to different pollutants, while remote management optimises maintenance and reduces operational costs. These innovative solutions ensure a rapid response to leaks and anomalous emissions, improving air quality and minimising environmental impact.
Conclusion: solutions for a more sustainable future in the oil industry
Commitment to reducing emissions and protecting the environment is now an unavoidable priority for the oil industry. Precise air quality monitoring, through the use of advanced technologies like Kunak solutions, allows refineries to minimise their environmental impact and comply with the strictest regulations. Investing in real-time measurement systems and innovative control strategies not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures the sustainability of the sector, contributing to a future where energy production and environmental respect go hand in hand.
Sources and references
Adebiyi, F.M. (2022) – Air quality and management in petroleum refining industry: A review.
Al-Rubaye, A.H., et al. (2023) – The side effect of oil refineries on environment: as a mini review.
Damian, C. (2013) – Environmental pollution in the petroleum refining industry.
Galván Rico, L., et al. (2007) – Los macroprocesos de la industria petrolera y sus consecuencias ambientales.
Granda, M.L., (2023) – Análisis de las emisiones en la articulación productiva de España: determinación de sectores clave en la contaminación del medio ambiente.
Monteiro, A., et al. (2017) – Towards an improved air quality index
Sojinu, S. O., & Ejeromedoghene, O. (2019) – Environmental challenges associated with processing of heavy crude oils.