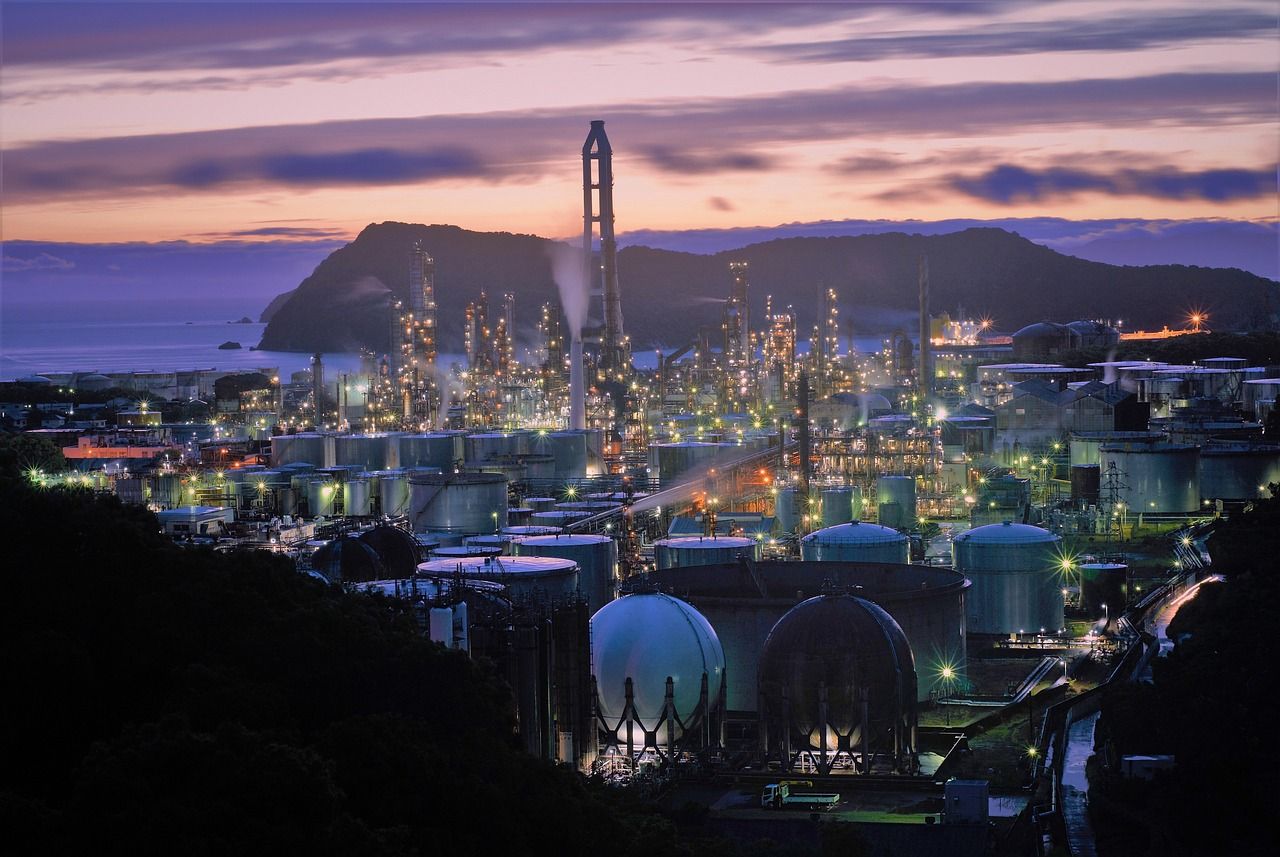
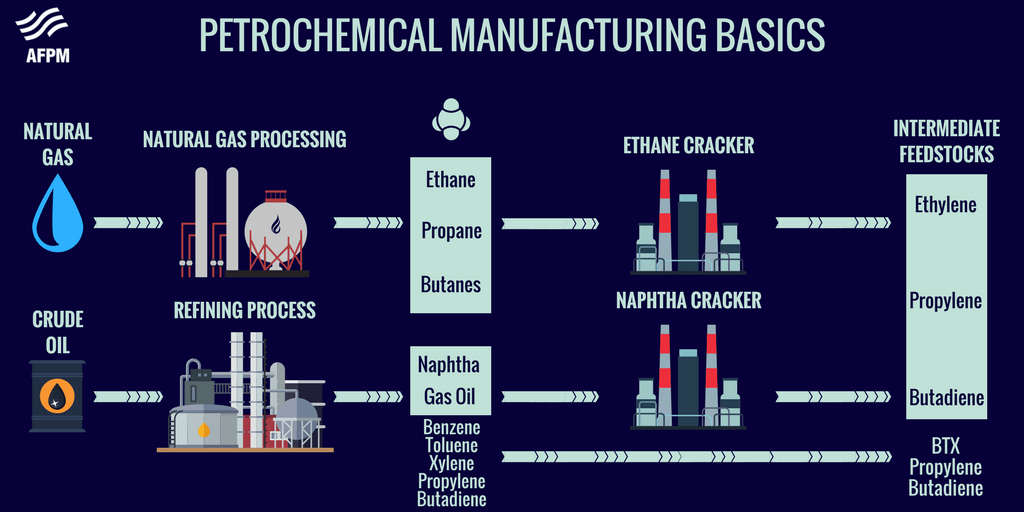
It is impossible to imagine a world without plastics, medicines, fertilizers, or fuels. The petrochemical industry is the backbone of modern life, providing the essential materials that sustain our daily lives. However, this progress comes at an invisible cost: a significant environmental impact that, in many cases, is devastating for people and biodiversity.
This article explores the environmental impact of the petrochemical industry, focusing on air pollution, its main pollutants, and how the most advanced air qualityAir quality refers to the state of the air we breathe and its composition in terms of pollutants present in the atmosphere. It is considered good when poll...
Read more monitoring solutions based on technological innovation, such as those from Kunak, stand out as the best allies to mitigate these effects.

Comparison of GHG emissions in the United States with respect to the petrochemical industry – Source EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency).
What is petrochemical pollution?
Petrochemical pollution comes from the release of harmful substances into the environment derived from petrochemical industry activities. It originates during the transformation of oil and natural gas into chemicals and raw materials for manufacturing countless everyday products. This pollution primarily affects the air but also damages water and soil. It is a significant source of atmospheric pollution that accelerates climate change and poses a severe risk to human health and ecosystems.
Main air pollutantsAir pollution caused by atmospheric contaminants is one of the most critical and complex environmental problems we face today, both because of its global r...
Read more from petrochemical plants
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Substances present in the air, such as benzene, toluene, and xylenes, which can cause respiratory problems and cancer.
- Greenhouse GasesWhile the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere has been steadily and rapidly increasing in recent decades, in May 2025, CO2 surpassed 43...
Read more (GHGs): Powerful gases like methane and carbon dioxide, the primary accelerators of global warming. - Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): By penetrating the bloodstream through the lungs, these particles cause respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): One of the main causes of acid rain.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Precursors of tropospheric ozone and smogSmog, beyond that dense fog
Smog is a mixture of air pollutants that accumulate in the atmosphere, especially in urban areas. This phenomenon is character...
Read more formation.
How does the petrochemical industry affect air quality?
The petrochemical industry is one of the primary sources of air pollution due to the chemical and physical processes involved in the extraction of raw materials, production, processing, and the trade of its manufactured products.
Main sources of air pollution in the petrochemical industry
There are various sources of emissions in the petrochemical industry, with oil refining being one of the most significant contributors to air pollution. This pollution occurs both near their complex industrial facilities and over long distances, as pollutants spread and drastically worsen the air quality that anyone can breathe.
Air Quality Innovation in Just 1 Click
Stay informed about the air you breathe!
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest updates on environmental monitoring technology, air quality studies, and more.
The main sources of air pollution emissions in the petrochemical industry include:
- Process Emissions: Techniques that involve separations, conversions, isomerizations, and treatments such as cracking (breaking large molecules into smaller ones), among others. These emissions enter the air through venting, sampling points, and safety valves.
- Combustion Emissions: Generated by burning fuels during the production and transportation of petrochemical materials. Their composition and volume vary depending on the type of fuel used. Most of these emissions come from fixed combustion sources such as furnaces, heaters, and steam boilers. Additionally, they can also originate from flares, devices activated intermittently to safely release hazardous substances during shutdowns or disruptions in industrial processes.
- Fugitive Emissions: Sudden vapor leaks from equipment or pipelines, as well as small continuous leaks from equipment seals. These can occur at any point in a petrochemical facility and are one of the main causes of air quality deterioration. Effective monitoring and control require advanced technology systems to provide continuous real-time detection.
- Storage and Handling Emissions: Released during the storage and handling of natural gas, oil, and their derivatives. This is a potential issue across all petrochemical product distribution points.
- Auxiliary Emissions: Originating from units such as cooling towers, boilers, sulfur recovery units, and wastewater treatment plants. Atmospheric emissionsAtmospheric emissions are pollutants emitted into the air, mainly as a result of human activities such as industry, transport by combustion vehicles and en...
Read more from cooling towers primarily consist of gases released when the aqueous phase comes into contact with air during the cooling process. In wastewater treatment plants, emissions may arise from the removal of VOCs from contaminated wastewater.
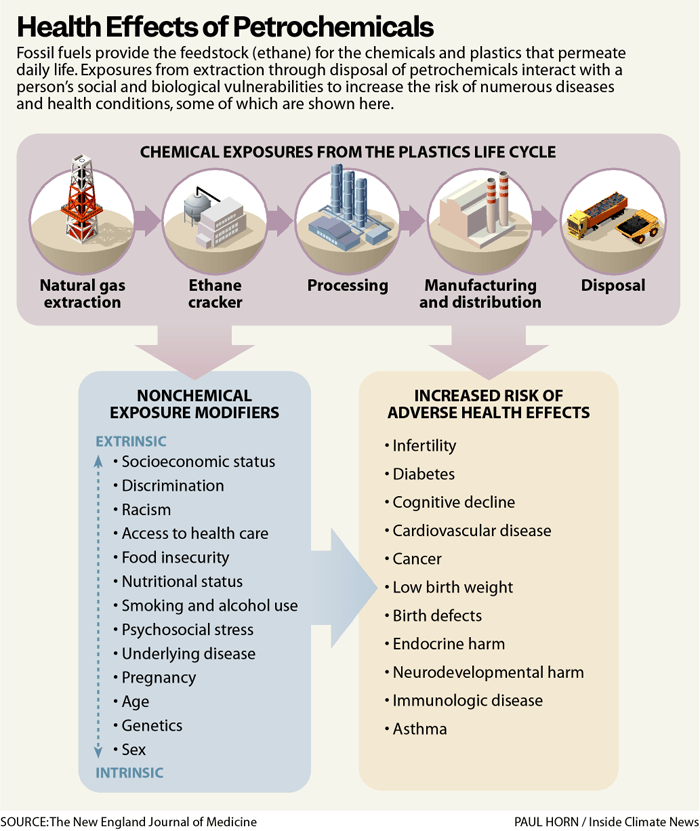
Public health effects of pollution from the petrochemical industry – Source The New England Journal of Medicine.
Health impacts of petrochemical emissions
Communities living near petrochemical plants are the first to be affected by the degradation of air quality due to high levels of PM2.5 particles, VOCs, and NOx emissions. This environmental situation most commonly impacts the most vulnerable populations (children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing conditions) and causes:
- Short-term exposure: Headaches, dizziness, and eye irritation.
- Long-term exposure: Respiratory diseases such as asthma, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions.
An example of the direct relationship between the increase in respiratory and cardiovascular diseases among residents living near petrochemical plants and their emissions—some of which are carcinogenic pollutants—is the case of Cancer Alley in LaPlace, Louisiana (USA).
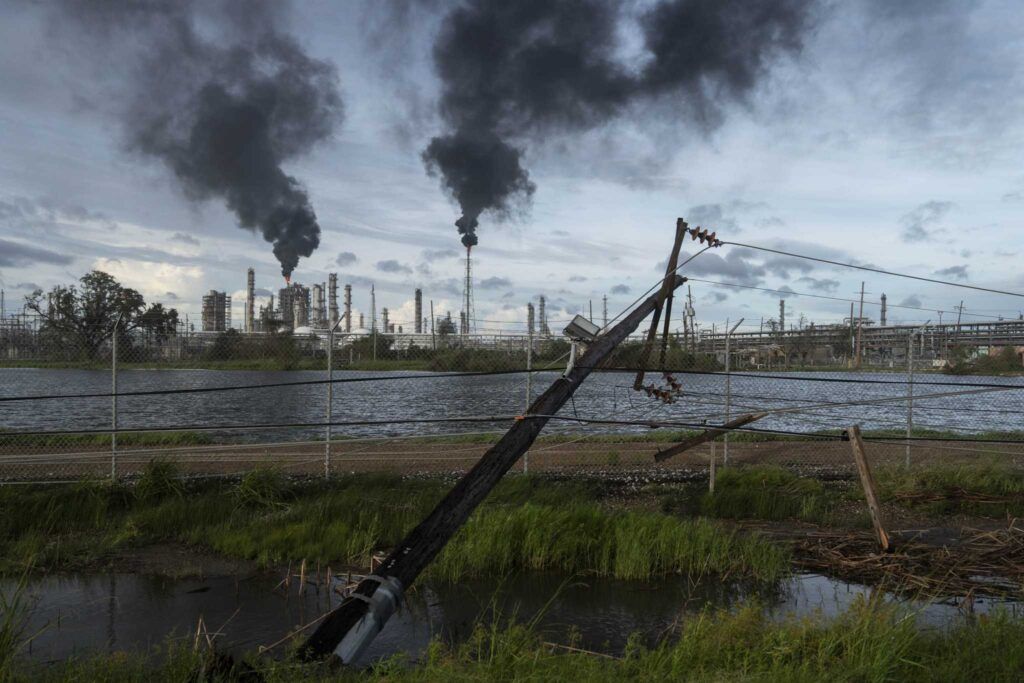

Oil refinery in LaPlace, Louisiana. USA Photo by Michael Robinson Chavez/The Washington Post via Getty Images
On the banks of the Mississippi, LaPlace is a populated area with a high concentration of petrochemical plants and refineries. In its environment, among other pollutants, levels of the VOC chloroprene (a volatile compound used in the manufacture of neoprene) have been detected up to 400 times higher than the limits established by the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency of the United States).
The presence of this carcinogen in the air has caused an alarming level of environmental pollution. It is responsible for a higher incidence of liver, lung, and kidney cancer among local residents, as well as the development of respiratory diseases due to exposure above recommended levels (0.2 µg/m³) of chloroprene.
Although petrochemical complexes and oil refineries are well-known sources of a wide range of environmental pollutants, the number of epidemiological and ecological studies aimed at evaluating the potential harmful health effects of living near these facilities is quite limited. Rovira, J., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M. and Domingo, J.L. (2021).
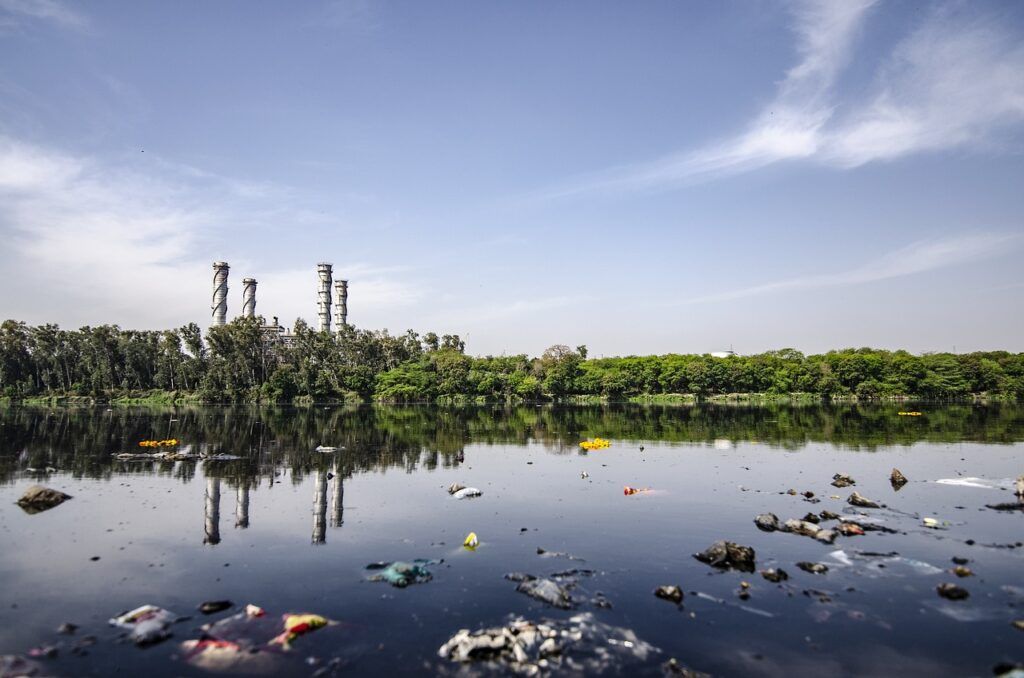

Water pollution in the vicinity of a petrochemical industry.
Environmental impact of the petrochemical industry
The environmental impact caused by the petrochemical industry goes beyond air pollution, extending to water and soil, damaging ecosystems and biodiversity, as well as accelerating climate change.
Water pollution
The petrochemical industry contaminates water bodies through chemical effluents, toxic spills from accidents, and the infiltration of pollutants. Together, they create highly toxic situations that threaten aquatic biodiversity and, in the most severe cases, accumulate in the food chain, ultimately reaching humans.
Soil pollution
Leaks and spills from the petrochemical industry can contaminate soil for decades. They affect soil fertility, cause degradation that makes it unsuitable for agricultural use, and promote desertification. Additionally, the alteration of the physical and chemical structure of the soil caused by petrochemical pollution impacts organisms linked to terrestrial ecosystems, reducing their resilience to climate change and ultimately compromising food security.
The contamination by trace elements in agricultural soils near petrochemical industrial complexes is a cause for concern due to the risk of accumulation in food systems and subsequent effects on human health. Cao, L. et al (2020).
Contribution to climate change
The petrochemical industry is one of the main sources of greenhouse gas emissions, which accelerate climate change. Its emissions release large amounts of carbon dioxide and methane, as well as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds that contribute to the formation of tropospheric ozone, a pollutant that is also a potent greenhouse gas.

Petrochemical industry and inhabited environments prompt environmental justice intervention.
Environmental justiceEnvironmental justice on air quality issues is crucial to ensure that all communities, especially those in areas of high traffic and industrial activity, a...
Read more and petrochemical pollution
The environmental issues associated with the petrochemical industry constitute one of the main challenges faced by environmental justice. This is because these industrial plants are often strategically located near communities that are more vulnerable in socioeconomic terms. Exposing these populations to the toxic emissions derived from petrochemical activities only exacerbates this spatial and social dynamic, increasing existing inequalities.
Petrochemical pollutants generate a clear social asymmetry in the distribution of environmental costs, perpetuating marginalization and social exclusion, to the detriment of the well-being that every person deserves by their universal right to health, with access to clean air, water, and soil.
An example of this situation is the Houston Ship Channel in Texas, United States. This channel, which stretches over 80 kilometers from the city of Houston to the Gulf of Mexico, is home to the largest concentration of petrochemical industries in the country and the world. The intense industrial activity generates high levels of air pollution, considered among the worst in the country.
Additionally, there is a concerning pattern: the most polluting facilities tend to be located near communities composed of ethnic minorities and low-income residents. This exacerbates social inequalities and exposes these groups to greater health risks, leading to a higher incidence of respiratory diseases and cancer, as well as disrupting the ecological balance.
The role of air quality monitoringControlling air quality is an essential task in order to enjoy optimal environmental conditions for healthy human development and to keep the environment i...
Read more in petrochemical plants
Continuous air quality monitoring is essential to ensure emission control, early leak detection, and the prevention of pollution episodes in petrochemical plants.
In the petrochemical industry, it is necessary to strengthen institutional capacities, adopt advanced monitoring technologies, and promote corporate social responsibility to achieve sustainable environmental compliance. Audu, A. J. and Umana, A. U. (2024).
The implementation of advanced technologies, such as those developed by Kunak, allows for the continuous and real-time collection of data on multiple pollutants with high precision. This facilitates informed decision-making by both plant operators and environmental regulators. These solutions not only help comply with environmental regulations but also contribute to minimizing the environmental impact of petrochemical activities, optimizing processes, and reducing environmental risks for nearby communities.
How Kunak solutions help petrochemical facilities
Real-time monitoring of VOCs and methane
Kunak solutions address one of the main challenges of petrochemical plants: detecting fugitive emissions immediately. This enables a rapid response to avoid environmental impacts and public health risks. This capability is crucial, as many of these compounds are precursors to tropospheric ozone and contribute to global warming.
Air quality control at the perimeter
Through continuous monitoring of atmospheric pollutants in sensitive areas (facility boundaries or areas near populations), it ensures that pollution levels do not exceed permitted thresholds. Kunak offers systems for perimeter surveillance in industries that measure key parameters accurately and continuously, providing reliable data to assess environmental impact and take corrective measures when necessary.
Remote data management
Kunak’s cloud platform allows for the visualization, analysis, and reporting of air quality data remotely. It facilitates real-time supervision and streamlines report generation for authorities and affected communities. This accessibility to data promotes transparency and environmental justice while improving efficiency in environmental management.
Early alerts
This is one of the most innovative aspects of Kunak’s solutions. They are designed to notify relevant stakeholders quickly and efficiently when preset pollutant levels are exceeded. Immediate activation enables the deployment of appropriate corrective measures to mitigate adverse environmental and public health impacts as soon as possible.
Optimization of industrial processes
Based on the implementation of advanced technologies, it facilitates the early identification of critical episodes such as leaks or deviations from operational parameters. This is achieved through the integration of continuous monitoring systems and early alerts that detect any production irregularities in real time. Precise and timely identification of these anomalies allows for the immediate activation of corrective action protocols. It prevents greater damage, minimizes environmental impact, reduces operational costs, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations while promoting continuous improvement in industrial processes.
In summary, Kunak’s monitoring solutions not only improve production processes and the environmental performance of petrochemical plants but also contribute to public health protection and compliance with environmental regulations. Focused on precision, accessibility, and prevention, Kunak’s air quality monitoring solutions are an indispensable tool for the petrochemical industry in its transition toward more sustainable and environmentally and socially responsible processes.

Air monitoring with Kunak technology systems at BASF plant in Ludwigshafen (Germany) – Kunak
Success story in air quality monitoring in industrial perimeters
A success story in air quality monitoring in petrochemical industrial environments, aimed at avoiding the significant impact this industry can have on the environment, the well-being of the local population, and regulatory compliance, is that of the global chemical industry leader, BASF. They requested the implementation of Kunak’s advanced air monitoring technology for their Ludwigshafen plant (Germany) to enhance their environmental management strategy.
Kunak’s innovative technology has provided this chemical plant, considered one of the largest in Europe, with flexible and reliable monitoring. By complementing the existing monitoring network with real-time data analysis in the cloud, BASF has been able to better detect emissions, projecting a cleaner and more environmentally and socially responsible business approach. At the same time, it has fostered compliance with environmental regulations and the development of a rapid and efficient response to production process anomalies.
The results obtained leave no doubt: the strong correlation between the data provided by the Kunak sensors, in a scalable and sustainable way over time, has allowed BASF to better detect its emissions, projecting a cleaner and more environmentally and socially responsible business approach. At the same time, it has fostered, ensured compliance with environmental regulations and developed a fast and efficient response to anomalies in production processes.
Regulations and standards for petrochemical emissions
Petrochemical industries are subject to international, national, and regional regulations and standards. These control and reduce atmospheric pollutant emissions to protect public health, preserve the environment, and promote more sustainable petrochemical industrial practices. Compliance with these regulations requires reliable monitoring technologies that provide accurate and continuous data, a function perfectly fulfilled by Kunak’s environmental monitoring solutions.
Beyond technological innovation, they promote transparency and corporate social responsibility. It is a coordinated effort between governments, companies, and communities to ensure a balance between industrial development and environmental protection. The most relevant regulatory frameworks are:
EPA’s national emission standards for hazardous air pollutants (NESHAPs) (USA)
These are a set of regulations established by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Clean Air Act. They are designed to control emissions of hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) common in petrochemical operations.
Industrial emissions Directive (IED) of the European Union
This is the European Union’s primary regulation for controlling emissions from industrial facilities, including petrochemical plants. The IED is based on the Best Available Techniques (BAT) approach to promote the use of more efficient and less polluting technologies and industrial practices. The IED has driven a significant reduction in petrochemical industrial emissions in Europe, fostering technological innovation and sustainability in the sector. Additionally, it has contributed to harmonizing environmental standards across EU member states, facilitating a more coherent approach to environmental protection.
World Health Organization Air Quality Guidelines
These are global, evidence-based recommendations for establishing safe levels of exposure to key air pollutants. Although not binding, they serve as a reference for countries to develop their own national regulations to assess the impact of petrochemical emissions on air quality and public health. The WHO guidelines have been instrumental in raising awareness about the risks of air pollution and promoting global actions to improve air quality. Similarly, they have driven the adoption of more ambitious policies in many countries, including stricter standards for petrochemical industrial emissions.
Future challenges and solutions for petrochemical pollution
Adoption of low-emission technologies
The petrochemical industry faces the challenge of reducing its environmental footprint. However, their implementation alone does not guarantee the elimination of emissions. Air monitoring is essential to verify the effectiveness of these technologies and identify failures in control systems and optimization in their operation.
Transition to renewable raw materials
A promising solution to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. However, this process can generate secondary emissions. This is where air monitoring becomes crucial to assess the real impact and ensure that air quality in nearby communities is not compromised.
Implementation of fugitive emission detection systems
A significant challenge due to their unpredictable and dispersed nature. Identifying and quantifying these emissions in real time requires continuous monitoring. This not only reduces environmental impact but also improves operational efficiency and helps comply with environmental regulations.
Community air quality control projects
The involvement of local communities in air quality monitoring projects is essential to ensure transparency and environmental justice. It allows citizens to access real-time data on pollutant levels, empowering them to make informed decisions and demand concrete actions. Additionally, it strengthens collaboration between industry, governments, and communities, fostering trust and facilitating the implementation of more effective and sustainable solutions.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What are the main pollutants emitted by petrochemical plants?
Petrochemical plants primarily emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM2.5), and methane gas (CH4). These pollutants are harmful to both human health and the environment. Additionally, VOCs and methane contribute to global warming and tropospheric ozone formation. NOx and PM2.5 have been directly linked to respiratory, cardiovascular, and other health issues. Monitoring and controlling these emissions from the petrochemical industry is essential to protect the air we breathe and reduce their environmental impact.
How does air pollution from petrochemical plants affect nearby communities?
Residents near petrochemical plants are exposed to higher risks of developing respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and cancer due to prolonged exposure to pollutants emitted by these facilities. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor air quality and take measures to reduce emissions from this industry to protect the health of nearby communities.
What technologies are used to monitor air pollution in petrochemical plants?
Advanced technologies such as the Kunak AIR Pro, a monitoring system that uses sensors to measure various pollutants in real time, are employed. In the petrochemical industry, they are effective in measuring volatile organic compounds, methane, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, they facilitate proactive emission control, helping to identify leaks, optimize processes, and comply with environmental regulations. Continuous monitoring is key to reducing environmental impact and protecting the health of nearby communities.
What regulations control emissions from petrochemical plants?
In the United States, NESHAPs (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants), established by the EPA, set strict limits for toxic pollutants. In Europe, emissions are regulated under the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), which establishes requirements to minimize environmental impact. These regulations aim to protect public health and the environment, ensuring that petrochemical plants operate in a cleaner and more sustainable manner.
How can continuous air quality monitoring improve environmental compliance?
Continuous air quality monitoring enables the detection of leaks, real-time emission tracking, and the generation of reports that facilitate compliance with environmental regulations. An affordable technological tool that helps identify and correct problems quickly, while providing and analyzing accurate data to ensure operations remain within legal limits. It is the path to promoting more responsible and transparent management, reducing environmental impact, and avoiding penalties.
Conclusion
The petrochemical industry is a significant source of air pollution and, therefore, an urgent environmental challenge, as it has a substantial impact on human health and ecosystems. However, the adoption of air quality monitoring measures, such as those provided by Kunak’s advanced technology, allows for the control of emissions, the protection of populations and the most vulnerable communities, and compliance with current environmental regulations. Investing in air quality technology that operates continuously, accurately, and in real time is preparing for a healthy future that does not compromise public health or the environment.
References
- Cottom, J.W., Cook, E. & Velis, C.A. A local-to-global emissions inventory of macroplastic pollution. Nature 633, 101–108 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07758-6
- Galván, L., Reyes, R. E., Guédez, C. y De Armas, D. Los macroprocesos de la industria petrolera y sus consecuencias ambientales. Universidad, Ciencia y Tecnología. 2017; 11(43), 091-097. http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1316-48212007000200006&lng=es&tlng=es
- Ragothaman, A., Anderson, WA. Air Quality Impacts of Petroleum Refining and Petrochemical Industries. Environments. 2017; 4(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments4030066
- Demetillo, M.A., Navarro, A. et al. Observing Nitrogen Dioxide Air Pollution Inequality Using High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Measurements in Houston, Texas. Environmental Science & Technology 2020 54 (16). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.0c01864
- Audu, A. J., Umana, A. U. The role of environmental compliance in oil and gas production: A critical assessment of pollution control strategies in the Nigerian petrochemical industry. International Journal of Scientific Research Updates, 2024. 8(2), 036-047. https://shibata.yubetsu.com/article/xYfoc49Y
- Rovira, J., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M. and Domingo, J.L. Environmental impact and human health risks of air pollutants near a large chemical/petrochemical complex: Case study in Tarragona, Spain, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 787, 2021, 147550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147550
- Smith, J. et al. Air quality impacts of petrochemical facilities in the Houston Ship Channel region: A case study using high-resolution monitoring and dispersion modeling. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5246571_Cumulative_Cancer_Risk_from_Air_Pollution_in_Houston_Disparities_in_Risk_Burden_and_Social_Disadvantage
- Zhang, Q., et al. Air pollution from petrochemical plants and its health effects. Environmental Research. Volume 263, Part A, 2020, 114414. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0269749120303924